Incoterms

Incoterms (English Incoterms, International commerce terms) are international rules in the format of a dictionary that provide unambiguous interpretations of the most widely used trade terms in the field of foreign trade, primarily with respect to the Franco - the place of transfer of responsibility from the seller to the buyer. International trade terms are standard terms of international sales contracts that are defined in advance in an internationally recognized document.
MAIN ABBREVIATIONS OF LOADING/UNLOADING CONDITIONS:
CY (Container Yard) – container terminal
FIFO (Free in free out) – loading and unloading are not included in the container transportation rate.
FILO (Free in/Liner out) – loading is not included in the rate, unloading is included in the rate.
LIFO (Liner in/Free out) – loading is enabled, unloading is not enabled.
LILO (Liner in/Liner out) – loading and unloading are included in the rate.
FCL (Full Container Load) - container loading by one sender to the address of one recipient.
LCL (Less Container Loading)– loading by one consignor of cargo intended for different consignees.
CY (Container Yard) – container terminal
FIFO (Free in free out) – loading and unloading are not included in the container transportation rate.
FILO (Free in/Liner out) – loading is not included in the rate, unloading is included in the rate.
LIFO (Liner in/Free out) – loading is enabled, unloading is not enabled.
LILO (Liner in/Liner out) – loading and unloading are included in the rate.
FCL (Full Container Load) - container loading by one sender to the address of one recipient.
LCL (Less Container Loading)– loading by one consignor of cargo intended for different consignees.
ADDITIONAL CHARGES APPLIED TO THE FREIGHT RATE:
THC (Terminal Handling Charges) - terminal handling charge. Terminal handling refers to loading (oTHC - at the port of departure) or unloading from the ship (dTHC - at the port of destination). It can also be denoted by the Russian abbreviation PRR (loading and unloading).
ALL IN - this wording means that the quoted rate includes all surcharges.
BAF (Bunker Adjustment Factor) is a surcharge determined by the cost of fuel on the international market.
BAS (=BFR) – basic, base rate;
CAF (Currency Adjustment Factor)- exchange rate surcharge. Most often it is some percentage of the base rate.
DF (=DOCS) is the surcharge associated with processing documents at the port of departure (ODF) or destination (DDF).
EMF (Equipment Management Fee) - equipment management fee;
ERS (Emergency Risk Surcharge) - a fee for unforeseen expenses. May also be called oTA (charges at the port of departure), dTA (charges at the port of destination);
OTA (Origin Transport Arbitrary) - contingency fee at the port of origin;
IMO Surcharge - a fee for the carriage of dangerous goods;
SEC (= ISPS, PSI) - security charge in the port;
SER Carrier Security Charge - a surcharge for the security of cargo during transportation.
GRI - increase in the base rate. Usually entered from some date.
Heavy Lift Charge - a fee charged in case of exceeding the weight of the load.
PSS (Peak Season Surcharge) - a surcharge introduced during a period of growth in traffic (usually in summer, autumn).
PCS (Port Congestion Surcharge) is a fee charged for reloading port areas.
WNS Winter Surcharge is a fee charged on directions of freezing ports (for example, Kotka, Tallinn, St. Petersburg). Introduced, most often, from December 1.
WarRisk-war risk fee. It is levied in ports located in the zone of armed conflicts.
THC (Terminal Handling Charges) - terminal handling charge. Terminal handling refers to loading (oTHC - at the port of departure) or unloading from the ship (dTHC - at the port of destination). It can also be denoted by the Russian abbreviation PRR (loading and unloading).
ALL IN - this wording means that the quoted rate includes all surcharges.
BAF (Bunker Adjustment Factor) is a surcharge determined by the cost of fuel on the international market.
BAS (=BFR) – basic, base rate;
CAF (Currency Adjustment Factor)- exchange rate surcharge. Most often it is some percentage of the base rate.
DF (=DOCS) is the surcharge associated with processing documents at the port of departure (ODF) or destination (DDF).
EMF (Equipment Management Fee) - equipment management fee;
ERS (Emergency Risk Surcharge) - a fee for unforeseen expenses. May also be called oTA (charges at the port of departure), dTA (charges at the port of destination);
OTA (Origin Transport Arbitrary) - contingency fee at the port of origin;
IMO Surcharge - a fee for the carriage of dangerous goods;
SEC (= ISPS, PSI) - security charge in the port;
SER Carrier Security Charge - a surcharge for the security of cargo during transportation.
GRI - increase in the base rate. Usually entered from some date.
Heavy Lift Charge - a fee charged in case of exceeding the weight of the load.
PSS (Peak Season Surcharge) - a surcharge introduced during a period of growth in traffic (usually in summer, autumn).
PCS (Port Congestion Surcharge) is a fee charged for reloading port areas.
WNS Winter Surcharge is a fee charged on directions of freezing ports (for example, Kotka, Tallinn, St. Petersburg). Introduced, most often, from December 1.
WarRisk-war risk fee. It is levied in ports located in the zone of armed conflicts.
ADDITIONAL CHARGES APPLIED TO CARGO IN PORT:
Demurrage - a penalty charged for overuse of a container. For import, this period is calculated from the day it is unloaded at the terminal until the day the empty container is returned to the port. For export, demurrage is considered from the day the empty container was received for loading until the day the loaded container was loaded onto the vessel.
Detention is a part of demurrage, which denotes the use of a container from the day it is taken out of the terminal until the day the empty container is returned to the port.
Storage (Storage) - a fee for excess storage of cargo in the port. Calculated from the day of unloading to the day of export of cargo from the terminal (inclusive).
Inspection– fee for work on moving the container to the inspection site (customs, veterinary, etc.).
MIDK - a fee for the work of moving a container to the site for an inspection and screening operation based on the use of ionizing radiation to obtain an x-ray image of cargo.
Demurrage - a penalty charged for overuse of a container. For import, this period is calculated from the day it is unloaded at the terminal until the day the empty container is returned to the port. For export, demurrage is considered from the day the empty container was received for loading until the day the loaded container was loaded onto the vessel.
Detention is a part of demurrage, which denotes the use of a container from the day it is taken out of the terminal until the day the empty container is returned to the port.
Storage (Storage) - a fee for excess storage of cargo in the port. Calculated from the day of unloading to the day of export of cargo from the terminal (inclusive).
Inspection– fee for work on moving the container to the inspection site (customs, veterinary, etc.).
MIDK - a fee for the work of moving a container to the site for an inspection and screening operation based on the use of ionizing radiation to obtain an x-ray image of cargo.
Also in Incoterms 2010 defines 4 terms applicable exclusively to maritime transport and transport of territorial waters:
1. FOB (free on board): goods are shipped to the buyer's ship, transshipment is paid by the seller.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight charges: buyer
Insurance: buyer.
2. FAS (free alongside ship): goods delivered to buyer's ship, contract states port of loading, transshipment and loading charges paid by buyer.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight charges: buyer
Insurance: Buyer.
3. CFR (cost and freight): Goods are delivered to the buyer's port of destination named in the contract.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight costs: buyer
Insurance costs: buyer.
Costs of shipping from the arrival terminal to the agreed warehouse: buyer.
4. CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight): the same as CFR, but the seller insures the main carriage.
1. FOB (free on board): goods are shipped to the buyer's ship, transshipment is paid by the seller.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight charges: buyer
Insurance: buyer.
2. FAS (free alongside ship): goods delivered to buyer's ship, contract states port of loading, transshipment and loading charges paid by buyer.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight charges: buyer
Insurance: Buyer.
3. CFR (cost and freight): Goods are delivered to the buyer's port of destination named in the contract.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Freight costs: buyer
Insurance costs: buyer.
Costs of shipping from the arrival terminal to the agreed warehouse: buyer.
4. CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight): the same as CFR, but the seller insures the main carriage.
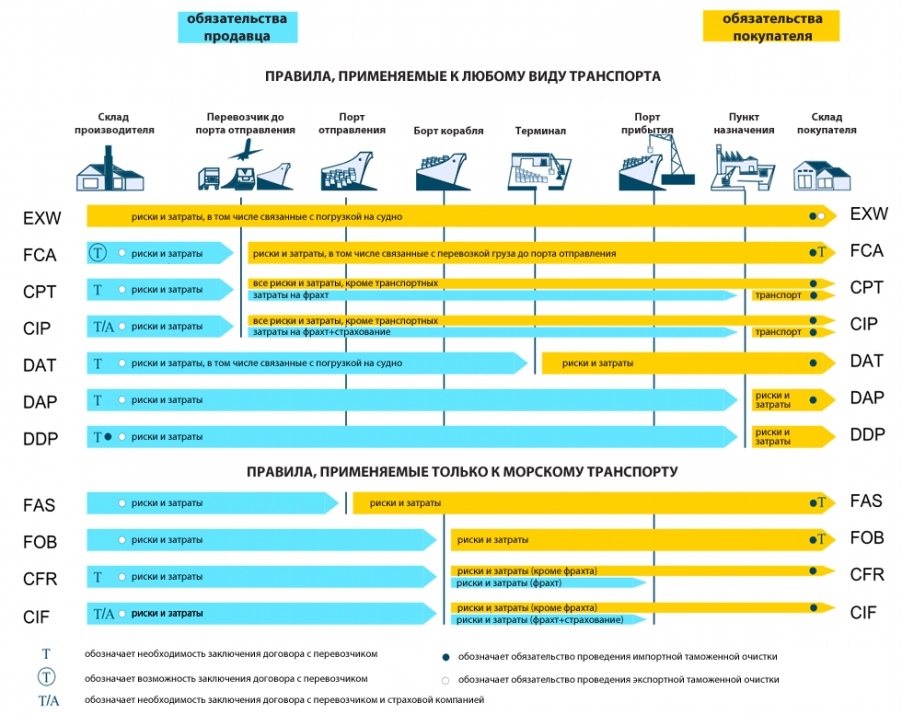
2010 INCOTERMS TERMS
Incoterms terms are three-letter abbreviations. The first letter indicates the moment of transfer of obligations for the goods from the seller to the buyer.
So,
- E - at the seller's warehouse
- F - at the terminal of departure of the main transportation (for example, if the transportation is by sea, then at the port terminal), the main transportation is not paid.
- C - at the main carriage arrival terminals, the main carriage is paid
- D - at the buyer's warehouse.
Incoterms terms are three-letter abbreviations. The first letter indicates the moment of transfer of obligations for the goods from the seller to the buyer.
So,
- E - at the seller's warehouse
- F - at the terminal of departure of the main transportation (for example, if the transportation is by sea, then at the port terminal), the main transportation is not paid.
- C - at the main carriage arrival terminals, the main carriage is paid
- D - at the buyer's warehouse.
The Incoterms-2010 rules define 11 terms. Most of them apply to any type of transportation.
1. EXW (ex works): the goods are taken by the buyer from the seller's warehouse specified in the contract. Who pays the costs:
Export duties: the buyer.
Import duties: Buyer.
Main freight charges: Buyer.
Insurance costs: buyer.
2. FCA (free carrier): the goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer to the terminal of departure specified in the contract,
Export duties: the seller.
Import duties: Buyer.
Main freight charges: Buyer.
Insurance costs: buyer.
3. CPT (carriage paid to): the goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.
4. CIP (carriage and insurance paid to): the same as CPT, but the main carriage is insured by the seller.
5. DAT (delivered at terminal): delivery to the import customs terminal specified in the contract is paid.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic freight costs: seller
Insurance costs: seller.
6. DAP (delivered at point): delivery to the destination specified in the contract, import duties and local taxes are paid by the buyer.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.
Costs for the delivery of goods from the terminal of arrival to the agreed warehouse: the seller.
7. DDP (delivered duty paid): the goods are delivered to the customer at the destination specified in the contract, cleared of all duties and risks.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: seller.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.
1. EXW (ex works): the goods are taken by the buyer from the seller's warehouse specified in the contract. Who pays the costs:
Export duties: the buyer.
Import duties: Buyer.
Main freight charges: Buyer.
Insurance costs: buyer.
2. FCA (free carrier): the goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer to the terminal of departure specified in the contract,
Export duties: the seller.
Import duties: Buyer.
Main freight charges: Buyer.
Insurance costs: buyer.
3. CPT (carriage paid to): the goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.
4. CIP (carriage and insurance paid to): the same as CPT, but the main carriage is insured by the seller.
5. DAT (delivered at terminal): delivery to the import customs terminal specified in the contract is paid.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic freight costs: seller
Insurance costs: seller.
6. DAP (delivered at point): delivery to the destination specified in the contract, import duties and local taxes are paid by the buyer.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: buyer.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.
Costs for the delivery of goods from the terminal of arrival to the agreed warehouse: the seller.
7. DDP (delivered duty paid): the goods are delivered to the customer at the destination specified in the contract, cleared of all duties and risks.
Export duties: seller
Import duties: seller.
Basic transportation costs: seller
Insurance costs: buyer.



